Autonomous Public Transportation: Transforming Urban Mobility in Tartu
Introduction video
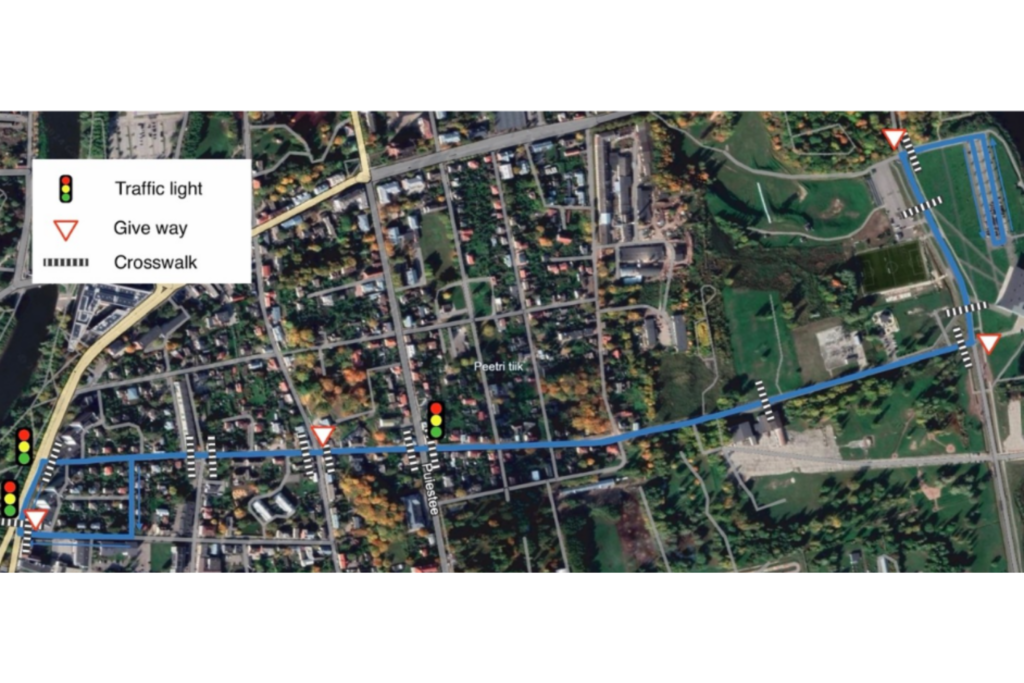
Route map
Collaboration of the tech companies
Auve Tech collaborated with the City of Tartu, Yazaki, and Avanti R&D to bring autonomous public transportation solutions to the European Capital of Culture. This case study delves into the real-traffic testing of the MiCa and Iseauto autonomous shuttles, exploring the project’s objectives, operational challenges, and impactful results over 92 days of deployment.
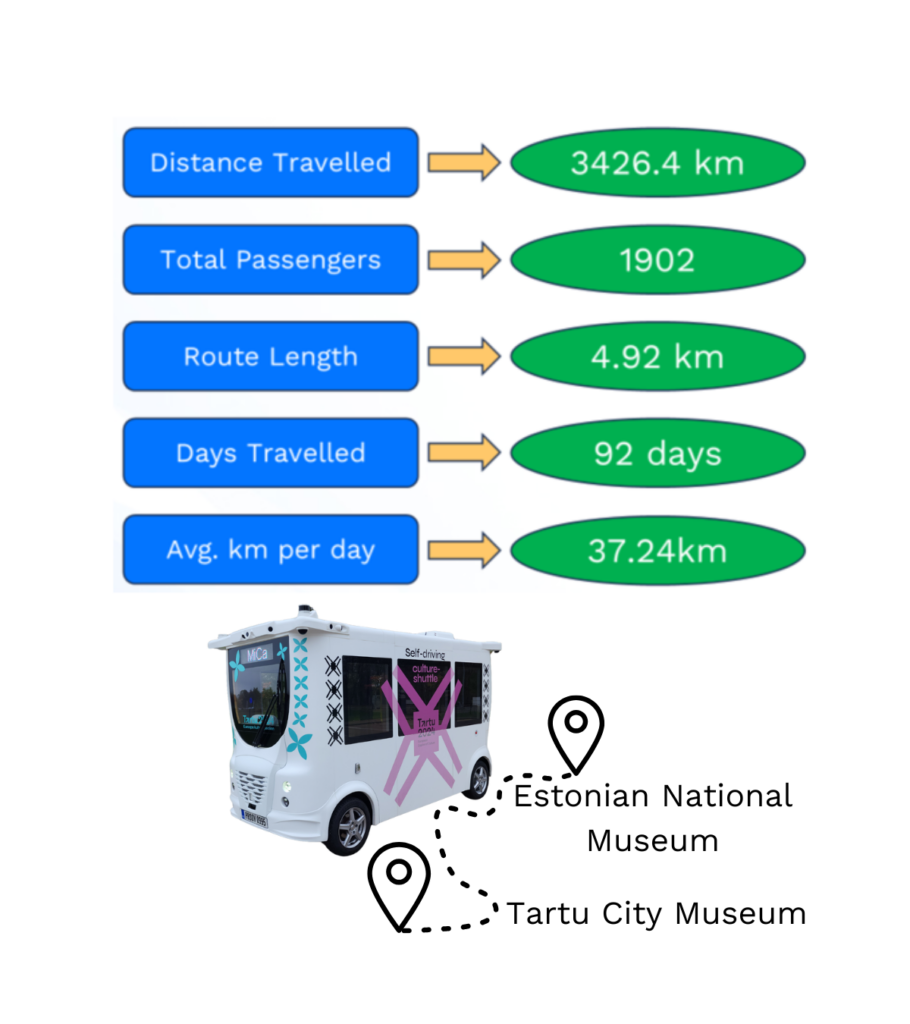
Tartu, the European Capital of Culture 2024, served as an ideal testing ground for innovative transport solutions. The project connected two major cultural landmarks, the Estonian National Museum (ERM) and Tartu City Museum, through a 4.92 km route.

Operating Evironment and Problem
The shuttles operated in open, mixed traffic, navigating urban roads under the following conditions:
- Speed Limits: 50 km/h (road), with shuttles capped at 20 km/h.
- Intersections:
- Main Roads: 5
- Give Way Signs: 3
- Traffic Lights: 3
- Priority to the right Intersections: 11
- Pedestrian Crossings: 14
- Schedule: Departured every 30 minutes from Tuesday-Saturday 11am-3pm, completing 8 daily rounds.
Bus Stops: Integrated into the route for accessibility – 2 stops
Tartu faced typical urban mobility challenges:
- Inefficient public transport in low-demand areas.
- Expanding mobility options for individuals with limited access.
- The need for sustainable solutions that reduce carbon footprints.

Goals and Solution
Goals: The project aimed to:
- Ensure reliable autonomous public transportation with daily availability of shuttles across 92 days.
- Operate efficiently under diverse weather and road conditions.
- Demonstrate the feasibility of autonomous public transportation in mixed-traffic conditions.
- Showcase the scalability and public acceptance of autonomous shuttles.
- Collect data to refine autonomous solutions for future deployments.
Solution: Auve Tech deployed MiCa and Iseauto shuttles with advanced features to address Tartu’s needs for autonomous transportaion solution:
- Safety: Operations capped at 20 km/h in urban environments.
- Flexibility: Adaptable schedules connecting key cultural landmarks.
- Sustainability: Electric-powered shuttles designed for low environmental impact.
- Smart Navigation: Tackled complex intersections and pedestrian crossings seamlessly.
Collaborators Yazaki and Avanti R&D played pivotal roles in integrating advanced electric and AI systems, ensuring reliability under real-world conditions.

Execution
Autonomous public transportation project was executed in stages:
- Planning and Mapping: Designing a 4.92 km route optimized for public transport needs.
- Testing: Evaluating shuttle performance in mixed traffic, focusing on intersections and crossings.
- Deployment: Seamless operations for 92 days, serving passengers with consistent reliability.
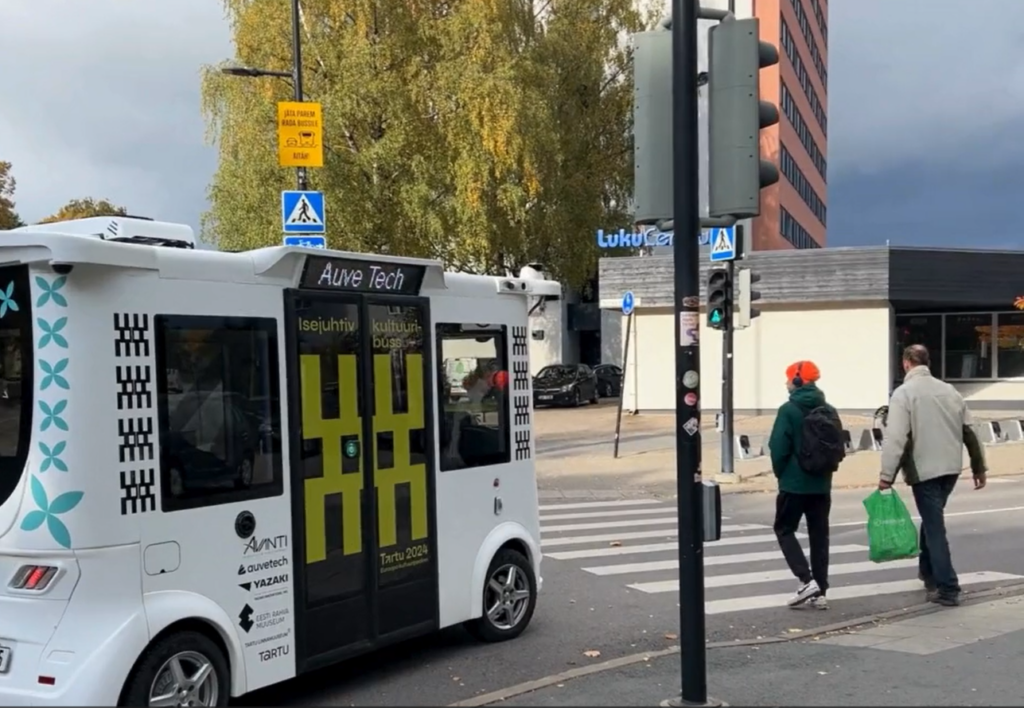

Challenges and Outcomes
Challenges
- Adapting to diverse weather conditions, including rain and fluctuating temperatures.
- Navigating complex urban environments with mixed traffic.
- Integrating seamlessly with existing public transportation systems.
- Handling unexpected obstacles such as roadworks or sudden detours.
- Managing public perceptions and building trust in autonomous technologies.
- Providing reliable performance in areas with limited connectivity.
- Ensuring robust cybersecurity to protect vehicle systems and data.
Quantitative Outcomes
- Distance Traveled: 3426.4 km across 92 days of operation.
- Passengers Served: 1902 passengers experienced the future of autonomous public transportation.
- Route Efficiency: Successfully navigated a 4.92 km route with zero disruptions.
Qualitative Outcomes
- Positioned Tartu as a leader in smart mobility innovation.
- Improved accessibility for the community, especially underserved groups.
- Generated valuable insights for scaling autonomous mobility solutions.
Lessons Learned
Strategic:
- Effective collaboration with partners was key to the project’s success.
- Public feedback shaped future development plans for autonomous public transportation.
Technical:
- Enhanced mapping and AI algorithms improved shuttle performance in urban settings.
- Real-world testing highlighted areas for improving teleoperations and weather adaptability.
Conclusion:
The Tartu project highlighted the transformative potential of autonomous public transportation, paving the way for smarter, more accessible cities. Auve Tech invites urban planners and organizations to collaborate on shaping the future of mobility.
Contact Us hello@auve.tech to explore how Auve Tech can help your city.
